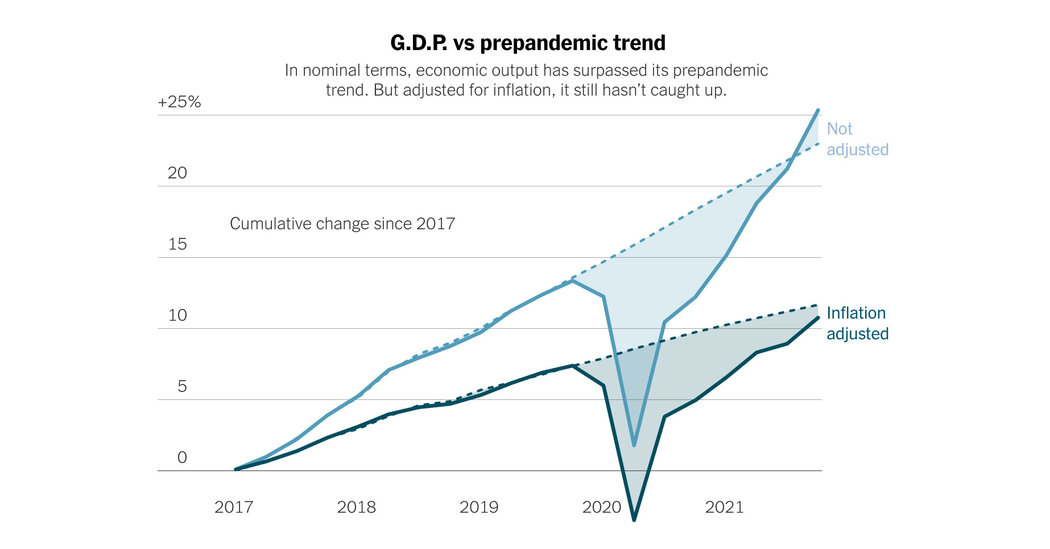
Here’s a notable fact about the U.S. economic recovery: Inflation-adjusted output last quarter was just 1 percent below where it would have been if the pandemic had never happened.
Here’s another one: Ignoring inflation, output is 1.7 percent above where it would have been absent the coronavirus.
Those two facts help explain the confusing, contradictory nature of the late-pandemic economy. On the one hand, the recovery has been remarkably swift by both historical standards and compared with what forecasters expected when the crisis began. On the other hand, a surprising surge in inflation is preventing the economy from rebounding more quickly, or feeling more normal. And to some extent, the same forces — the remarkable levels of aid provided by the government, and the unusual nature of the pandemic recession itself — are responsible for both trends.
The chart below helps tell the story. Inflation-adjusted gross domestic product (the dark blue line) has rebounded sharply since the early months of the crisis, but has yet to return to its prepandemic trend. That might not seem too surprising; businesses have mostly reopened, but the pandemic is still restraining daily activities, at least for many people.
But the second line on the chart, in light blue, shows that the story is a bit more complicated than that. In non-inflation-adjusted terms, gross domestic product — in simple terms, everything we make and spend in a given three-month period — has surged significantly beyond its pre-Covid trend. In dollar terms, we are producing and spending as much as ever. But because of inflation, those dollars are worth less than before.
The basic story here is simple. The reopening of the economy after the initial lockdowns brought a surge in demand, which was bolstered by the trillions of dollars in aid that the federal government provided to households and businesses. But supply chain bottlenecks, labor shortages and other issues meant that businesses could not fully meet that demand. Strong demand plus limited supply is a recipe for inflation.
What happens next is less clear. If companies are able to hire more workers and pick up production, then supply will be able to meet demand. In that scenario, the dark blue line would start to look more like the light blue one — growth would be strong in terms of real output, not just nominal dollars.
But if supplies can’t rebound, then either we will continue to burn off excess demand in the form of inflation, or demand will have to fall. Either scenario would make it harder for the economy to rebound fully from the shock of the pandemic.